A Closer Look at the Big Data Dangerous Meanings

Big Data Dangerous Meanings “Big data” has become a synonym for expansion, innovation, and productivity in the digital age. Businesses utilize vast volumes of data to get insights, make wise decisions, and foster innovation.However, behind the surface of this data-driven transformation is a complex world rife with unknown dangers. This essay explores the nuanced meaning of big data, pointing out potential benefits and drawbacks associated with its widespread use.
Understanding Big Data
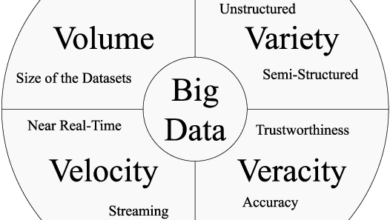
The term “big data” describes the massive volume of data generated daily by various digital channels, such as social media, online transactions, and sensors. Three typically used variables (volume, velocity, and variety) are used to characterize this data.The abundance, velocity of creation, and variety of data forms make it an invaluable resource for comprehending the world.
The Upbeat Attitude of Big Data
Even with all of the talk about the risks that come with big data, it is important to recognize the benefits as well. Big data gives organizations, scholars, and legislators access to never-before-seen tools for process optimization, pattern analysis, and trend prediction. The capacity to derive significant insights from extensive datasets promotes creativity, effectiveness, and well-informed choices, which in turn propels advancements across diverse domains.

Exposing the Dangers:
Privacy Issues:
Big Data Dangerous Meanings collecting is so ubiquitous that it creates serious privacy issues. The enormous amounts of personal information that businesses gather are vulnerable to misuse or unauthorized access. It’s difficult to strike a balance between safeguarding individuals’ privacy and using data to advance society.
Risks to Security:
One of the most important concerns is massive data repositories security. Because of how sophisticated attacks are becoming, there is a greater chance of data breaches. Unauthorized access to personal information can lead to financial losses, identity theft, and reputational damage to a person or organization.
Algorithmic Discrimination:
Algorithms play a major role in Big Data Dangerous Meanings analytics in order to interpret the massive volumes of data. These algorithms could, however, unintentionally reinforce prejudices found in the training set of data. This may lead to biased decisions that discriminate against certain people or groups.
Over-dependence on data
Over-reliance on Big Data Dangerous Meanings without taking into account its limits is a deadly trap. Putting all your faith in data-driven insights might result in making poor judgments. It’s critical to understand that while statistics might aid in decision-making, human judgment is still necessary.

Moral Conundrums:
Big Data Dangerous Meanings brings up moral concerns about information gathering and application. Ethical norms may not always coincide with what is lawful. For both individuals and organizations, striking a balance between the advancement of technology and upholding ethical standards is a constant issue.
Getting Across the Perilous Waters:
While big data may have certain drawbacks, it’s important to understand that taking preventative action may reduce those risks and open the door to responsible data use.
Putting in Place Sturdy Security Measures:
Prioritizing the deployment of strong cybersecurity solutions is important for organizations that want to protect theirBig Data Dangerous Meanings repositories. To find and fix flaws, frequent security audits, encryption, and access limits are all part of this.
Making Certain Ethical Data Procedures:
Setting clear ethical guidelines for the collection, storage, and application of data is crucial. Organizations should prioritize transparency and informed consent so that individuals have the freedom to choose how their data is used.
Handling Inaccurate Algorithms
It’s critical to routinely evaluate and improve algorithms in order to reduce algorithmic bias. This entails adding measurements for fairness, varying the training datasets, and including other viewpoints in the process of creation and assessment.
Encouraging Data Literacy
Encouraging a culture of data literacy guarantees that people comprehend the consequences of large-scale data. To enable users to make wise decisions in the digital world, this entails educating and training them on responsible data usage.
In summary:
Although big data offers a lot of positive potential, there are certain inherent concerns that should be carefully evaluated. By resolving privacy concerns, enhancing security protocols, addressing algorithmic biases, and promoting ethical data practices, we may fully exploit big data while mitigating its risks.The good news in this complex tango between innovation and accountability is that we can all work together to use big data to our advantage.